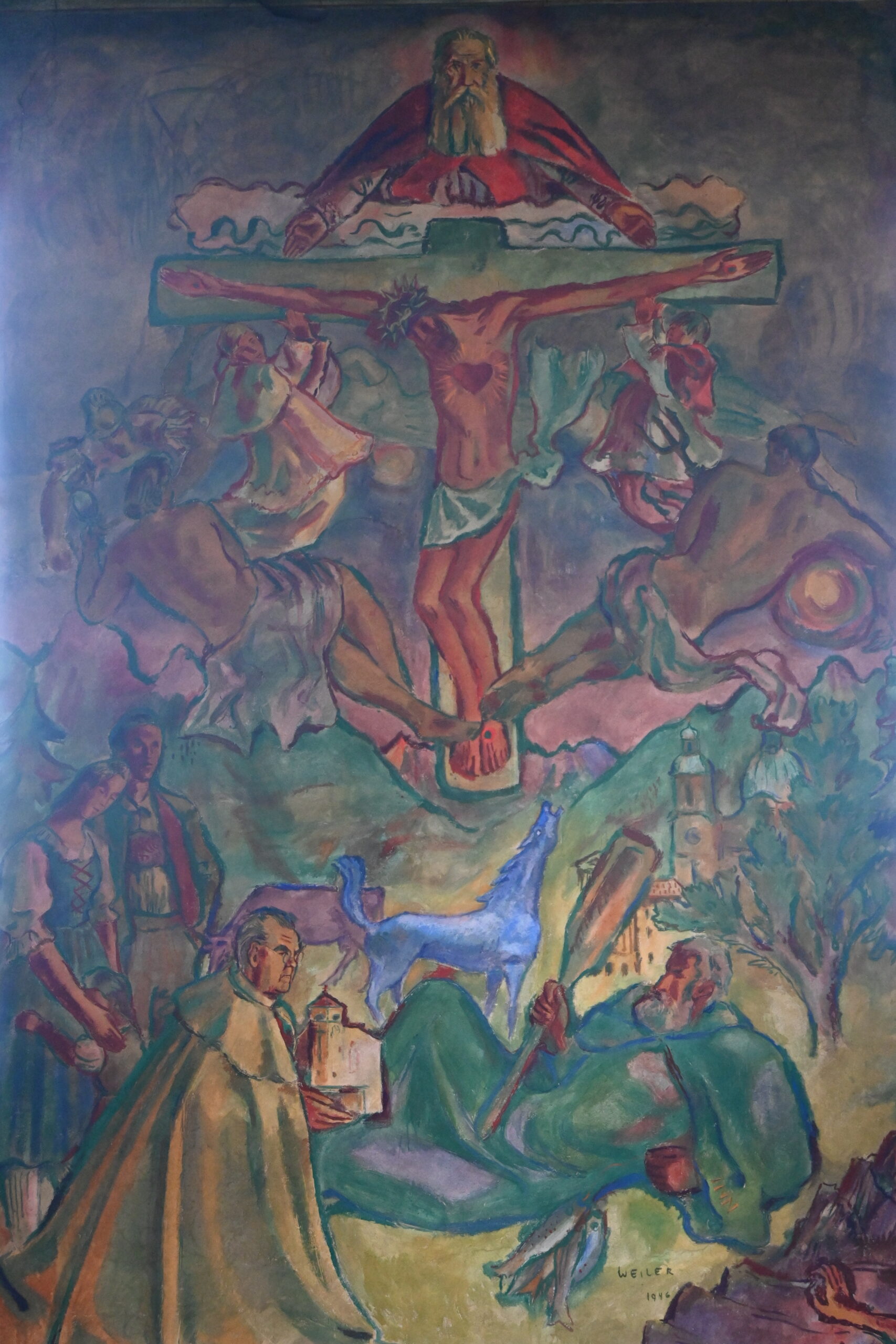Theresienkirche
Gramartstraße 4
Worth knowing
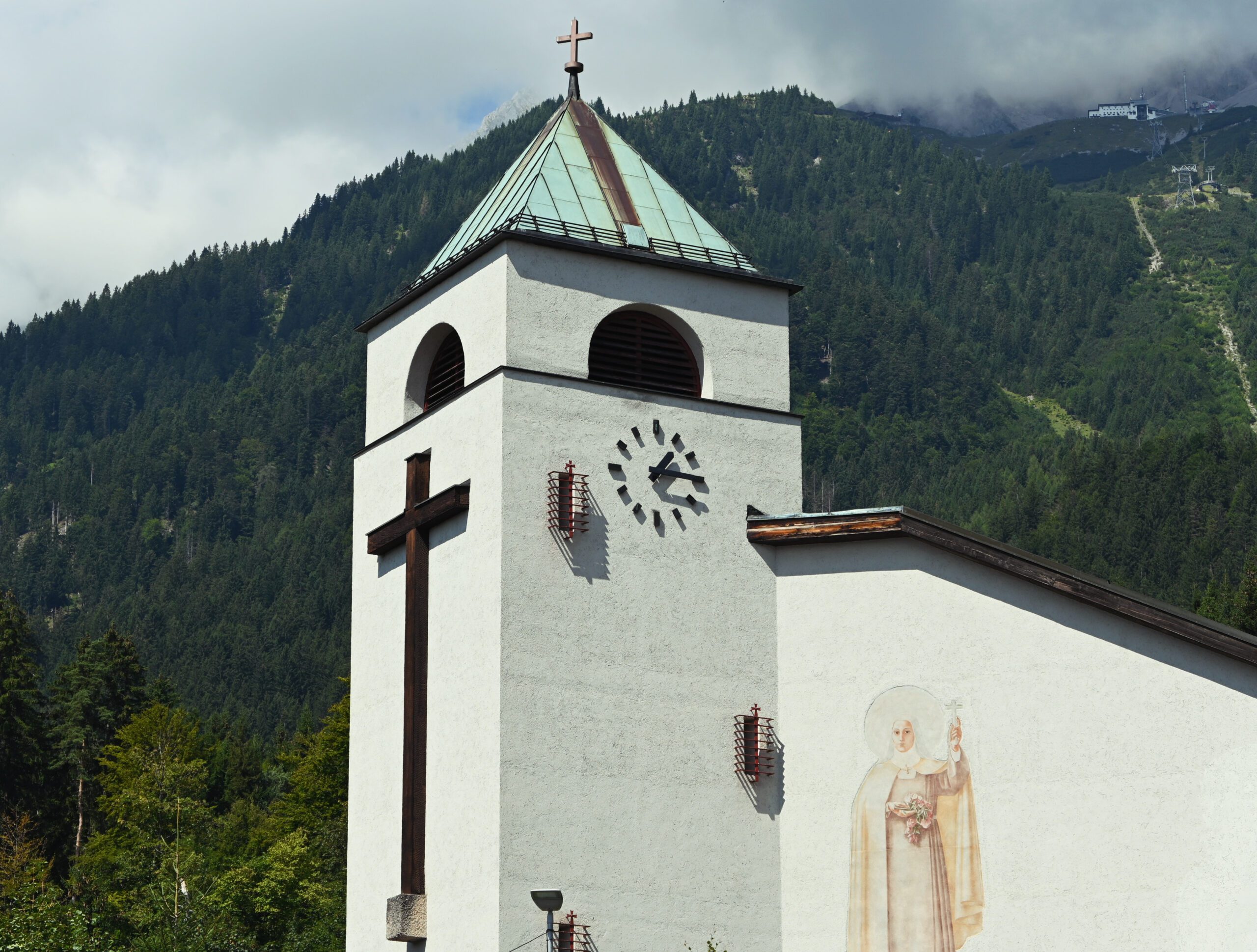
One floor above Innsbruck lies the pilgrimage church dedicated to Saint Thérèse of the Child Jesus. The history of this modest little church reflects the turbulent and changeable events of the first half of the 20th century and became the stage for what was perhaps the greatest art scandal in recent Tyrolean history. At the turn of the century, the Hungerburg had developed into an attraction for wealthy tourists and locals. The First World War and the economically difficult years that followed brought this lively scene to an abrupt end. Hungerburg had become a deserted residential area with only a handful of houses and no significant infrastructure. Nothing less than the first “miracle” that made the development of this new district possible was needed to breathe new life into “Hoch‑Innsbruck.” A few decades earlier, after discovering a water source on his land on the Hungerburg, Josef von Attlmayr had gratefully named his residence “Mariabrunn” in honor of the Virgin Mary, and this name quickly caught on in Catholic circles as the district’s designation. The Mariabrunn Church Association, founded in 1910 and named after this “miracle,” placed the fate of Hungerburg in the hands of a modern saint. In the 1920s, the devout members built a small chapel in a garden house around a relic and an image of Saint Thérèse. Thérèse of Lisieux had died only a few years earlier—after a short but exceptionally devout life—of tuberculosis, and had been canonized with remarkable speed by Pope Pius X. Around ten years after the war, when the period of hardship transitioned into a boom and Hungerburg once again became a popular travel and excursion destination thanks to renewed tourism and the construction of the Höhenstraße, the moral life of the locals—especially the youth—was also to be strengthened. In 1927, the Tiroler Anzeiger wrote:
“Mariabrunn urgently needs a church and a school! Not a magnificent building is required, but a simple little church in the familiar Tyrolean style, nestled in forest greenery on the hillside, whose bright bell calls the inhabitants of the entire Hungerburg plateau—locals and visitors alike—to worship, and invites Innsbruck’s mountain-loving youth to pause on their Sunday walks. A house of God as a visible gathering place for solemn and joyful occasions in the newly emerging community, alongside a simple schoolhouse for the youngest citizens of ‘Hoch‑Innsbruck,’ where they are to be raised not as class warriors, enemies of religion or property, but as upright Germans and Christian Tyroleans who love their homeland.”
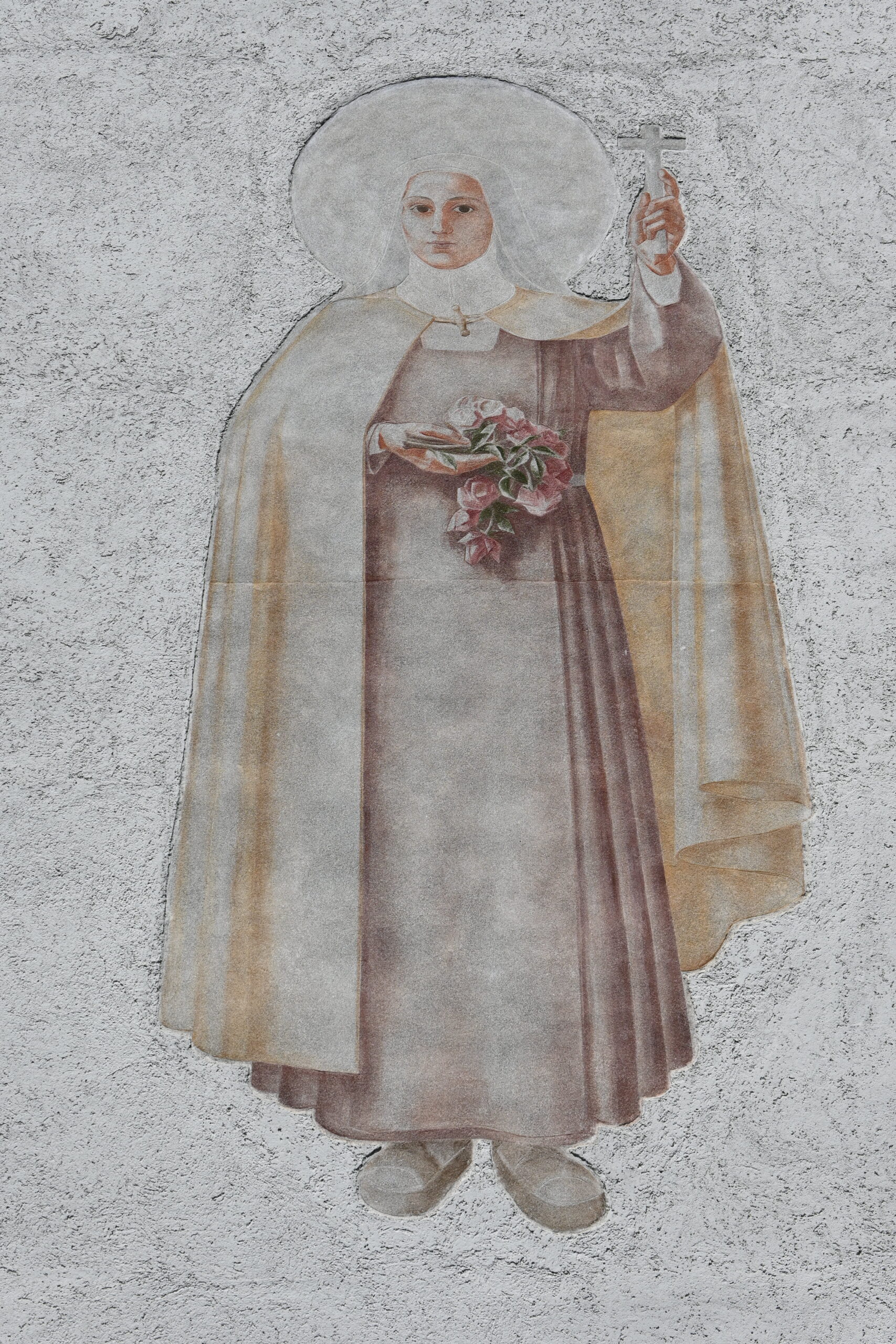
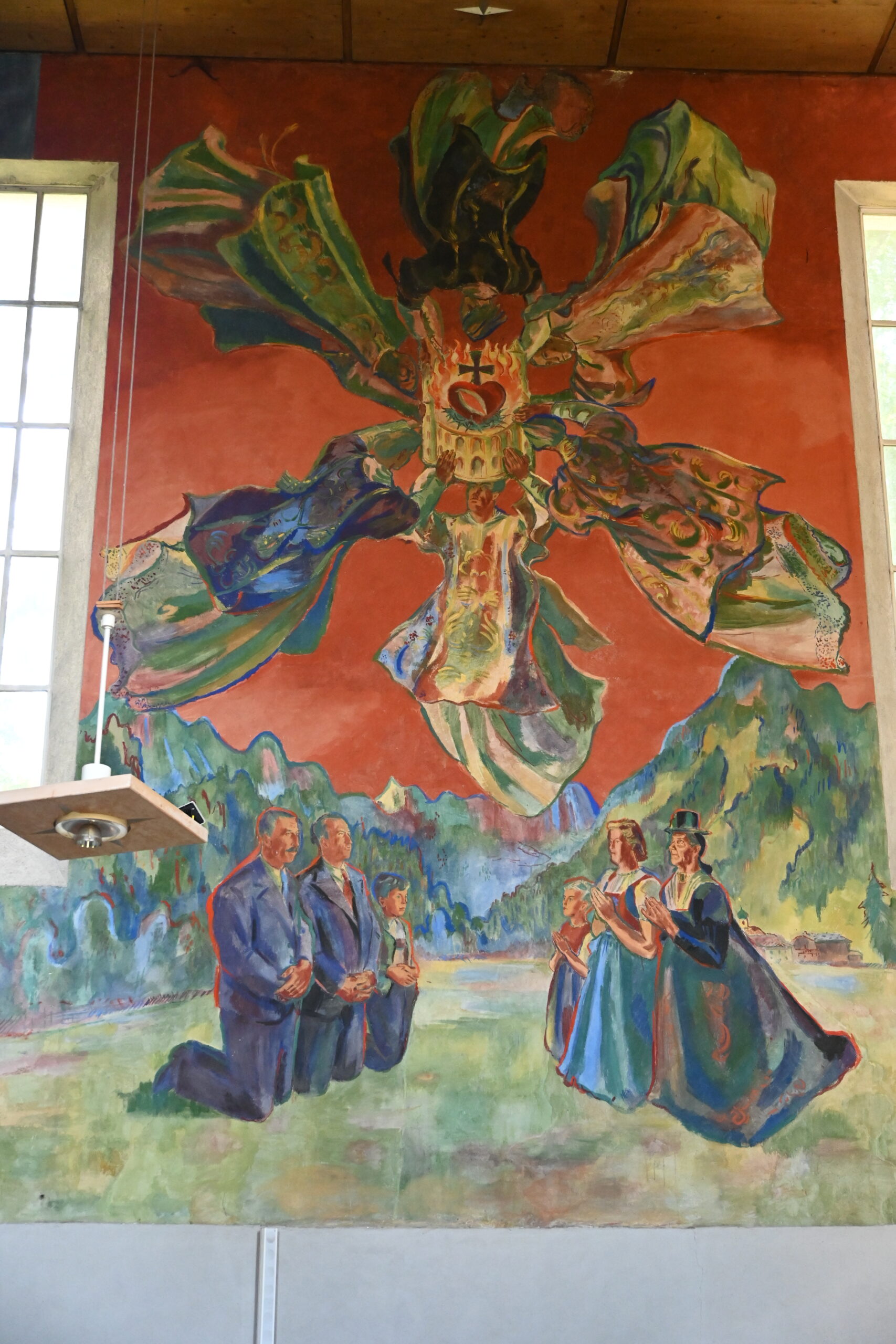
In 1931, the Mariabrunn Association launched an architectural competition. The Upper Austrian architect Wilhelm Stigler (1903–1976), who already ran his own office at Claudiaplatz in his early twenties, surprisingly won against established architects such as Clemens Holzmeister and Franz Baumann. However, since his plans exceeded the limited financial means—by then the economic crisis of the 1930s had struck—a more economical design by Siegfried Thurner was implemented. The cubic building followed the contemporary style of New Objectivity rather than the Tyrolean style desired by the Tiroler Anzeiger. The clock without numbers on the prominent tower was a popular stylistic element. After the building was completed in 1935, the Innsbruck‑based artist Ernst Nepo (1895–1971), who was sympathetic to both New Objectivity and fascism, created the fresco of Saint Thérèse above the entrance. The depiction already anticipated the artistic style favored under the National Socialist regime, which would dominate Austria from 1938 until the end of the war. After the war, Nepo’s involvement in the church’s completion was no longer desired; his history as the Tyrolean representative of the Nazi Reich Chamber of Fine Arts outweighed his undeniable artistic talent. Among other things, the early National Socialist had painted a portrait of Adolf Hitler as early as 1937—before the Anschluss—which had been presented to the Führer personally by the Tyrolean Nazi Women’s Association as a birthday gift.
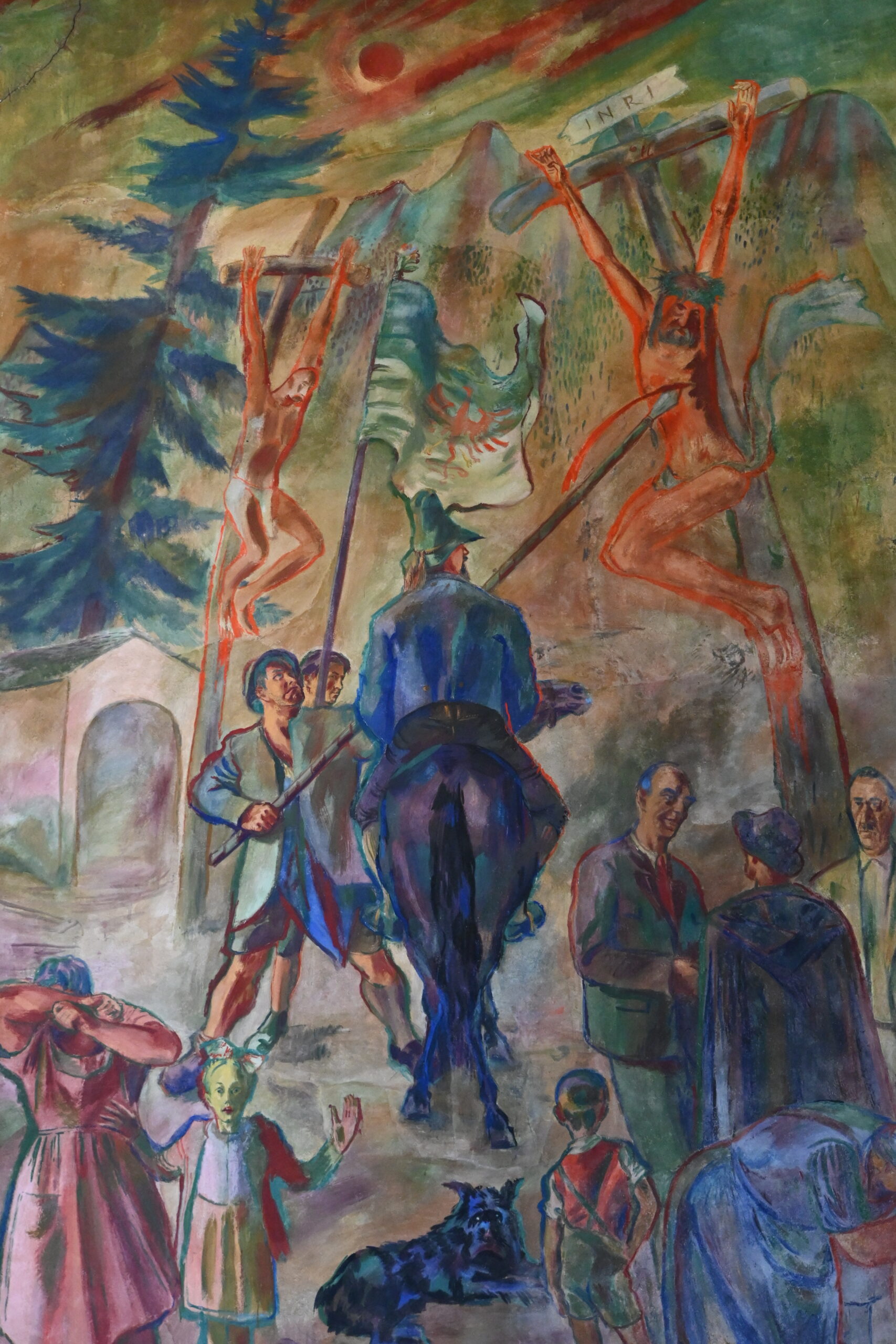
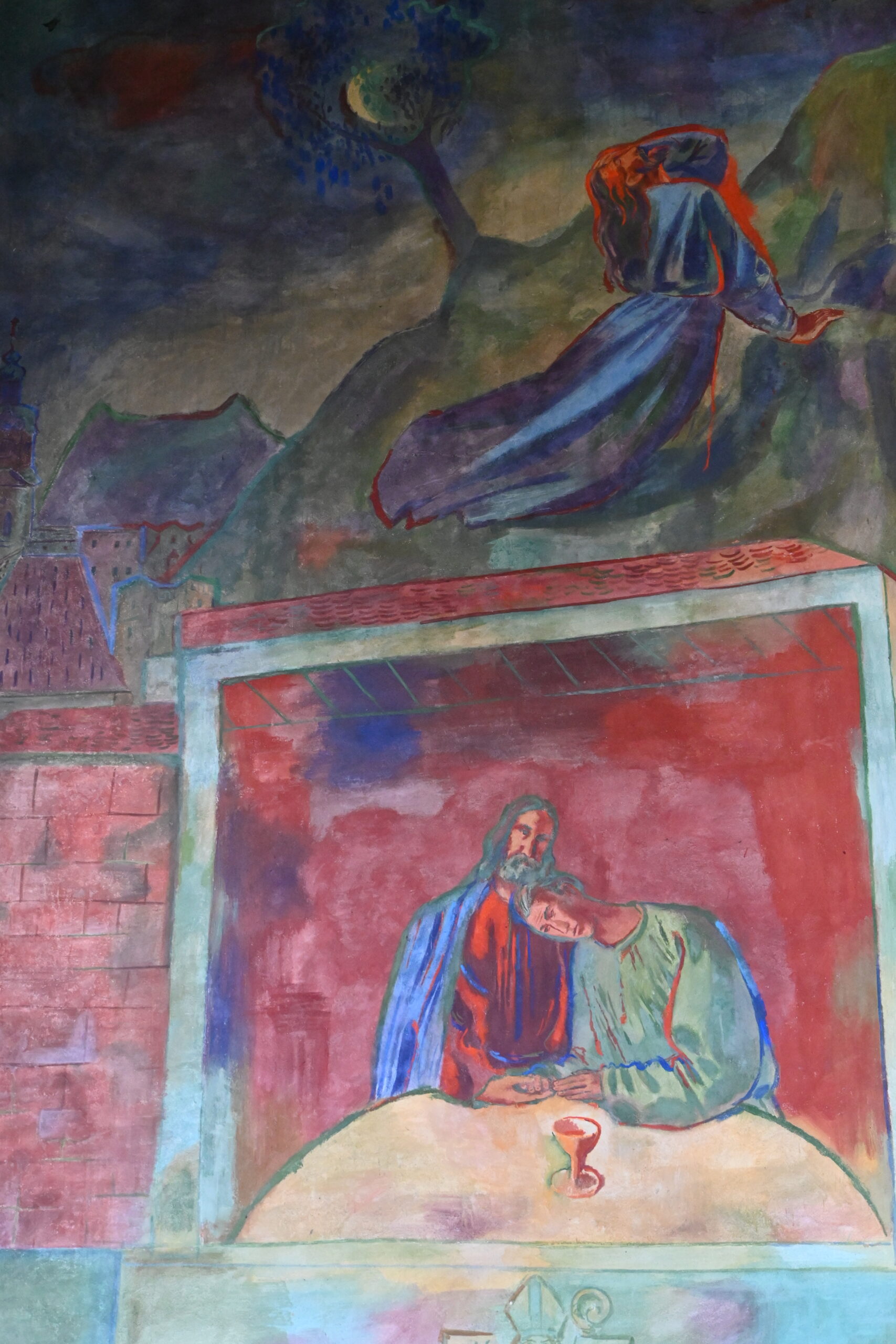
In his place, the Tyrolean artist Max Weiler (1910–2001) continued the work from 1946 onward, so that the nave would be decorated in time for the 150th anniversary of Tyrol’s renewal of the Sacred Heart Vow of 1796. Weiler, himself a silent follower of the system during the Nazi era, completed four paintings before he had to pause his work prematurely. “The Veneration of the Sacred Heart,” “The Sacred Heart Sun,” “Love of John and Gethsemane,” and “The Piercing of the Side” sparked a scandal that spread widely. The painting of the Sacred Heart Sun was mockingly dubbed the “Priests’ Carousel” due to its six flying clerics. The public was particularly dissatisfied with “The Piercing of the Side,” which depicted the onlookers at Christ’s last breath in traditional Tyrolean peasant clothing. One of the men beneath the cross bore a suspicious resemblance to Adolf Hitler, while a Tyrolean marksman thrust the spear into Christ’s side. A nude Venus had to be modestly painted over to quell the initial public outrage, which eventually led to a lawsuit filed by a farmer from Kössen, who claimed the painting disturbed religion and public order. Threats were made against both the artwork and the artist. The Tyrolean Farmers’ Association and parts of the Tyrolean clergy even forced Vatican intervention. After consultation between the Holy See in Rome and Tyrolean Bishop Paulus Rusch, a strict verdict followed: Completion of Weiler’s planned cycle of paintings was prohibited, and the unfinished sketches were never executed. For ten years, the existing artworks were hidden from public view behind a cloth. Today, the once‑scandalous Weiler paintings are proudly displayed and attract more visitors than Saint Thérèse herself.
Artikel Tiroler Anzeiger
Erschienen: 22. Jänner 1927 / Tiroler Anzeiger
Der heuer bevorstehende Bau zweier H ö h e n s t r a ß e n, — die zur polit. Gemeinde Mühlau gehörige Hungerburgsiedlung zum Stadtteile zu machen und die zur Innsbrucker Gemeinde gehörige Hungerburg mit den notwendigen Einrichtungen zu versehen — wird die Zeitforderungen der Gegenwart erfüllen helfen. Wenn der Bau dieser Straßen einmal restlos durchgeführt ist, dann wird das schöne Hochplateau der Hungerburg nicht nur eine sommerliche Erholungsstätte, sondern auch in den langen Wintermonaten zu einer glücklichen Insel werden, die ihren Wert in den letzten Zeiten oft schon deutlich gezeigt hat. Denn die Erfahrungen der letzten Jahre haben offensichtlich erwiesen, daß diese sonnige Terrasse über der Stadt Innsbruck während des ganzen Winters reicher an Licht und freundlichen Tagen ist als viele Siedlungen des Inntales. Man hat im Vorjahre mit Hilfe der Stadtgemeinde Innsbruck und insbesondere durch das großartige Entgegenkommen des Herrn Bürgermeisters Dr. Schumacher die Hungerburgstraße wiederholt offenhalten können. Man hat es gesehen, daß dieser Weg auch in strengen Winterzeiten eine sichere Verbindung zwischen Stadt und Hochplateau herzustellen vermochte. Das Glück, die Hungerburg im Winter besuchen zu können, wird künftig durch die vorgesehenen Verbesserungen der Straße noch erleichtert werden. Infolgedessen drängt die Zeit, die Kirche und die Schule, sowie einen Kindergarten auf dem Hungerburgplateau zu errichten. Denn dieses Werk ist eine Notwendigkeit. Die Hungerburg wird nach Errichtung beider Höhenstraßen wohl bald denselben Umfang nehmen wie andere Terrassenanlagen ähnlicher großer Städte. Die Siedlung auf der Hungerburg bringt aber notgedrungen eine Kirche und eine Schule mit sich. In dieser Hinsicht muß betont werden, daß schon lange Vorarbeiten geleistet wurden und daß man darauf hoffen darf, daß in nicht gar ferner Zeit dieses Werk zur Ausführung gelangt. Denn selbst die vornehmste und reichste materielle Kultur könnte nicht ersetzen, was der katholischen Bevölkerung an kirchlicher und schulischer Versorgung zusteht. Eine hochw. geistliche Stelle hat bereits erklärt, daß sie mitarbeiten wolle, und daß sie die Hoffnung hege, daß die Arbeiten bald gefördert werden könnten. Es wird nun an der gesamten Innsbrucker Bevölkerung liegen, durch tatkräftige Mitarbeit dieses Werk zu unterstützen. Insbesondere die Jugend wird die Vorzüge einer eigenen Kirche und Schule auf der Hungerburg erfahren. Viele Familien, die dort wohnen, müssen in die Stadt hinabsteigen, um den Gottesdienst oder die Schule zu besuchen. Dies ist besonders im Winter mit großen Beschwerden verbunden. Dieser Notstand muß behoben werden. Denn es ist Pflicht, den Bewohnern der Hungerburg die Vorteile und Bequemlichkeiten zu verschaffen, die eine moderne Zeit fordert.
The Red Bishop and Innsbruck's moral decay
In the 1950s, Innsbruck began to recover from the crisis and war years of the first half of the 20th century. On 15 May 1955, Federal Chancellor Leopold Figl declared with the famous words "Austria is free" and the signing of the State Treaty officially marked the political turning point. In many households, the "political turnaround" became established in the years known as Economic miracle moderate prosperity. Between 1953 and 1962, annual economic growth of over 6% allowed an increasing proportion of the population to dream of things that had long been exotic, such as refrigerators, their own bathroom or even a holiday in the south. This period brought not only material but also social change. People's desires became more outlandish with increasing prosperity and the lifestyle conveyed in advertising and the media. The phenomenon of a new youth culture began to spread gently amidst the grey society of small post-war Austria. The terms Teenager and "latchkey kid" entered the Austrian language in the 1950s. The big world came to Innsbruck via films. Cinema screenings and cinemas had already existed in Innsbruck at the turn of the century, but in the post-war period the programme was adapted to a young audience for the first time. Hardly anyone had a television set in their living room and the programme was meagre. The numerous cinemas courted the public's favour with scandalous films. From 1956, the magazine BRAVO. For the first time, there was a medium that was orientated towards the interests of young people. The first issue featured Marylin Monroe, with the question: „Marylin's curves also got married?“ The big stars of the early years were James Dean and Peter Kraus, before the Beatles took over in the 60s. After the Summer of Love Dr Sommer explained about love and sex. The church's omnipotent authority over the moral behaviour of adolescents began to crumble, albeit only slowly. The first photo love story with bare breasts did not follow until 1982. Until the 1970s, the opportunities for adolescent Innsbruckers were largely limited to pub parlours, shooting clubs and brass bands. Only gradually did bars, discos, nightclubs, pubs and event venues open. Events such as the 5 o'clock tea dance at the Sporthotel Igls attracted young people looking for a mate. The Cafe Central became the „second home of long-haired teenagers“, as the Tiroler Tageszeitung newspaper stated with horror in 1972. Establishments like the Falconry cellar in the Gilmstraße, the Uptown Jazzsalon in Hötting, the jazz club in the Hofgasse, the Clima Club in Saggen, the Scotch Club in the Angerzellgasse and the Tangent in Bruneckerstraße had nothing in common with the traditional Tyrolean beer and wine bar. The performances by the Rolling Stones and Deep Purple in the Olympic Hall in 1973 were the high point of Innsbruck's spring awakening for the time being. Innsbruck may not have become London or San Francisco, but it had at least breathed a breath of rock'n'roll. What is still anchored in cultural memory today as the '68 movement took place in the Holy Land hardly took place. Neither workers nor students took to the barricades in droves. The historian Fritz Keller described the „68 movement in Austria as "Mail fan“. Nevertheless, society was quietly and secretly changing. A look at the annual charts gives an indication of this. In 1964, it was still Chaplain Alfred Flury and Freddy with „Leave the little things“ and „Give me your word" and the Beatles with their German version of "Come, give me your hand who dominated the Top 10, musical tastes changed in the years leading up to the 1970s. Peter Alexander and Mireille Mathieu were still to be found in the charts. From 1967, however, it was international bands with foreign-language lyrics such as The Rolling Stones, Tom Jones, The Monkees, Scott McKenzie, Adriano Celentano or Simon and Garfunkel, who occupied the top positions in great density with partly socially critical lyrics.
This change provoked a backlash. The spearhead of the conservative counter-revolution was the Innsbruck bishop Paulus Rusch. Cigarettes, alcohol, overly permissive fashion, holidays abroad, working women, nightclubs, premarital sex, the 40-hour week, Sunday sporting events, dance evenings, mixed sexes in school and leisure - all of these things were strictly abhorrent to the strict churchman and follower of the Sacred Heart cult. Peter Paul Rusch was born in Munich in 1903 and grew up in Vorarlberg as the youngest of three children in a middle-class household. Both parents and his older sister died of tuberculosis before he reached adulthood. At the young age of 17, Rusch had to fend for himself early on in the meagre post-war period. Inflation had eaten up his father's inheritance, which could have financed his studies, in no time at all. Rusch worked for six years at the Bank for Tyrol and Vorarlberg, in order to finance his theological studies. He entered the Collegium Canisianum in 1927 and was ordained a priest of the Jesuit order six years later. His stellar career took the intelligent young man first to Lech and Hohenems as chaplain and then back to Innsbruck as head of the seminary. In 1938, he became titular bishop of Lykopolis and Apostolic Administrator for Tyrol and Vorarlberg. As the youngest bishop in Europe, he had to survive the harassment of the church by the National Socialist rulers. Although his critical attitude towards National Socialism was well known, Rusch himself was never imprisoned. Those in power were too afraid of turning the popular young bishop into a martyr.
After the war, the socially and politically committed bishop was at the forefront of reconstruction efforts. He wanted the church to have more influence on people's everyday lives again. His father had worked his way up from carpenter to architect and probably gave him a soft spot for the building industry. He also had his own experience at BTV. Thanks to his training as a banker, Rusch recognised the opportunities for the church to get involved and make a name for itself as a helper in times of need. It was not only the churches that had been damaged in the war that were rebuilt. The Catholic Youth under Rusch's leadership, was involved free of charge in the construction of the Heiligjahrsiedlung in the Höttinger Au. The diocese bought a building plot from the Ursuline order for this purpose. The loans for the settlers were advanced interest-free by the church. Decades later, his rustic approach to the housing issue would earn him the title of "Red Bishop" to the new home. In the modest little houses with self-catering gardens, in line with the ideas of the dogmatic and frugal "working-class bishop", 41 families, preferably with many children, found a new home.
By alleviating the housing shortage, the greatest threats in the Cold WarCommunism and socialism, from his community. The atheism prescribed by communism and the consumer-orientated capitalism that had swept into Western Europe from the USA after the war were anathema to him. In 1953, Rusch's book "Young worker, where to?". What sounds like revolutionary, left-wing reading from the Kremlin showed the principles of Christian social teaching, which castigated both capitalism and socialism. Families should live modestly in order to live in Christian harmony with the moderate financial means of a single father. Entrepreneurs, employees and workers were to form a peaceful unity. Co-operation instead of class warfare, the basis of today's social partnership. To each his own place in a Christian sense, a kind of modern feudal system that was already planned for use in Dollfuß's corporative state. He shared his political views with Governor Eduard Wallnöfer and Mayor Alois Lugger, who, together with the bishop, organised the Holy Trinity of conservative Tyrol at the time of the economic miracle. Rusch combined this with a latent Catholic anti-Semitism that was still widespread in Tyrol after 1945 and which, thanks to aberrations such as the veneration of the Anderle von Rinn has long been a tradition.
Education and training were of particular concern to the pugnacious Jesuit. The social formation across all classes by the soldiers of Christ could look back on a long tradition in Innsbruck. In 1909, the Jesuit priest and former prison chaplain Alois Mathiowitz (1853 - 1922) founded the Peter-Mayr-Bund. His approach was to put young people on the right path through leisure activities and sport and adults from working-class backgrounds through lectures and popular education. The workers' youth centre in Reichenauerstraße, which was built under his aegis, still serves as a youth centre and kindergarten today. Rusch also had experience with young people. In 1936, he was elected regional field master of the scouts in Vorarlberg. Despite a speech impediment, he was a charismatic guy and extremely popular with his young colleagues and teenagers. In his opinion, only a sound education under the wing of the church according to the Christian model could save the salvation of young people. In order to give young people a perspective and steer them in an orderly direction with a home and family, the Youth building society savings strengthened. In the parishes, kindergartens, youth centres and educational institutions such as the House of encounter on Rennweg in order to have education in the hands of the church right from the start. The vast majority of the social life of the city's young people did not take place in disreputable dive bars. Most young people simply didn't have the money to go out regularly. Many found their place in the more or less orderly channels of Catholic youth organisations. Alongside the ultra-conservative Bishop Rusch, a generation of liberal clerics grew up who became involved in youth work. In the 1960s and 70s, two church youth movements with great influence were active in Innsbruck. Sigmund Kripp and Meinrad Schumacher were responsible for this, who were able to win over teenagers and young adults with new approaches to education and a more open approach to sensitive topics such as sexuality and drugs. The education of the elite in the spirit of the Jesuit order was provided in Innsbruck from 1578 by the Marian Congregation. This youth organisation, still known today as the MK, took care of secondary school pupils. The MK had a strict hierarchical structure in order to give the young Soldaten Christi obedience from the very beginning. In 1959, Father Sigmund Kripp took over the leadership of the organisation. Under his leadership, the young people, with financial support from the church, state and parents and with a great deal of personal effort, set up projects such as the Mittergrathütte including its own material cable car in Kühtai and the legendary youth centre Kennedy House in the Sillgasse. Chancellor Klaus and members of the American embassy were present at the laying of the foundation stone for this youth centre, which was to become the largest of its kind in Europe with almost 1,500 members, as the building was dedicated to the first Catholic president of the USA, who had only recently been assassinated.
The other church youth organisation in Innsbruck was Z6. The city's youth chaplain, Chaplain Meinrad Schumacher, took care of the youth organisation as part of the Action 4-5-6 to all young people who are in the MK or the Catholic Student Union had no place. Working-class children and apprentices met in various youth centres such as Pradl or Reichenau before the new centre, also built by the members themselves, was opened at Zollerstraße 6 in 1971. Josef Windischer took over the management of the centre. The Z6 already had more to do with what Dennis Hopper and Peter Fonda were doing on the big screen on their motorbikes in Easy Rider was shown. Things were rougher here than in the MK. Rock gangs like the Santanas, petty criminals and drug addicts also spent their free time in Z6. While Schumacher reeled off his programme upstairs with the "good" youngsters, Windischer and the Outsiders the basement to help the lost sheep as much as possible.
At the end of the 1960s, both the MK and the Z6 decided to open up to non-members. Girls' and boys' groups were partially merged and non-members were also admitted. Although the two youth centres had different target groups, the concept was the same. Theological knowledge and Christian morals were taught in a playful, age-appropriate environment. Sections such as chess, football, hockey, basketball, music, cinema films and a party room catered to the young people's needs for games, sport and the removal of taboos surrounding their first sexual experiences. The youth centres offered a space where young people of both sexes could meet. However, the MK in particular remained an institution that had nothing to do with the wild life of the '68ers, as it is often portrayed in films. For example, dance courses did not take place during Advent, carnival or on Saturdays, and for under-17s they were forbidden.
Nevertheless, the youth centres went too far for Bishop Rusch. The critical articles in the MK newspaper We discuss, which reached a circulation of over 2,000 copies, found less and less favour. Solidarity with Vietnam was one thing, but criticism of marksmen and the army could not be tolerated. After years of disputes between the bishop and the youth centre, it came to a showdown in 1973. When Father Kripp published his book Farewell to tomorrow in which he reported on his pedagogical concept and the work in the MK, there were non-public proceedings within the diocese and the Jesuit order against the director of the youth centre. Despite massive protests from parents and members, Kripp was removed. Neither the intervention within the church by the eminent theologian Karl Rahner, nor a petition initiated by the artist Paul Flora, nor regional and national outrage in the press could save the overly liberal Father from the wrath of Rusch, who even secured the papal blessing from Rome for his removal from office.
In July 1974, the Z6 was also temporarily over. Articles about the contraceptive pill and the Z6 newspaper's criticism of the Catholic Church were too much for the strict bishop. Rusch had the keys to the youth centre changed without further ado, a method he also used at the Catholic Student Union when it got too close to a left-wing action group. The Tiroler Tageszeitung noted this in a small article on 1 August 1974:
"In recent weeks, there had been profound disputes between the educators and the bishop over fundamental issues. According to the bishop, the views expressed in "Z 6" were "no longer in line with church teaching". For example, the leadership of the centre granted young people absolute freedom of conscience without simultaneously recognising objective norms and also permitted sexual relations before marriage."
It was his adherence to conservative values and his stubbornness that damaged Rusch's reputation in the last 20 years of his life. When he was consecrated as the first bishop of the newly founded diocese of Innsbruck in 1964, times were changing. The progressive with practical life experience of the past was overtaken by the modern life of a new generation and the needs of the emerging consumer society. The bishop's constant criticism of the lifestyle of his flock and his stubborn adherence to his overly conservative values, coupled with some bizarre statements, turned the co-founder of development aid into a Brother in needthe young, hands-on bishop of the reconstruction, from the late 1960s onwards as a reason for leaving the church. His concept of repentance and penance took on bizarre forms. He demanded guilt and atonement from the Tyroleans for their misdemeanours during the Nazi era, but at the same time described the denazification laws as too far-reaching and strict. In response to the new sexual practices and abortion laws under Chancellor Kreisky, he said that girls and young women who have premature sexual intercourse are up to twelve times more likely to develop cancer of the mother's organs. Rusch described Hamburg as a cesspool of sin and he suspected that the simple minds of the Tyrolean population were not up to phenomena such as tourism and nightclubs and were tempted to immoral behaviour. He feared that technology and progress were making people too independent of God. He was strictly against the new custom of double income. People should be satisfied with a spiritual family home with a vegetable garden and not strive for more; women should concentrate on their traditional role as housewife and mother.
In 1973, after 35 years at the head of the church community in Tyrol and Innsbruck, Bishop Rusch was made an honorary citizen of the city of Innsbruck. He resigned from his office in 1981. In 1986, Innsbruck's first bishop was laid to rest in St Jakob's Cathedral. The Bishop Paul's Student Residence The church of St Peter Canisius in the Höttinger Au, which was built under him, commemorates him.
After its closure in 1974, the Z6 youth centre moved to Andreas-Hofer-Straße 11 before finding its current home in Dreiheiligenstraße, in the middle of the working-class district of the early modern period opposite the Pest Church. Jussuf Windischer remained in Innsbruck after working on social projects in Brazil. The father of four children continued to work with socially marginalised groups, was a lecturer at the Social Academy, prison chaplain and director of the Caritas Integration House in Innsbruck.
The MK also still exists today, even though the Kennedy House, which was converted into a Sigmund Kripp House was renamed, no longer exists. In 2005, Kripp was made an honorary citizen of the city of Innsbruck by his former sodalist and later deputy mayor, like Bishop Rusch before him.
Franz Baumann and Tyrolean modernism
The First World War not only brought ruling dynasties and empires to an end, the 1920s also saw many changes in art, music, literature and architecture. While jazz, atonal music and expressionism failed to establish themselves in little Innsbruck, a handful of architects changed the cityscape in an astonishing way. Inspired by new forms of design such as the Bauhaus style, skyscrapers from the USA and the Soviet Modernism from the revolutionary USSR, sensational projects emerged in Innsbruck. The best-known representatives of the avant-garde who brought about this new way of designing public space in Tyrol were Lois Welzenbacher, Siegfried Mazagg, Theodor Prachensky and Clemens Holzmeister. Each of these architects had their own idiosyncrasies, making the Tiroler Moderne nur schwer eindeutig zu definieren ist. Allen gemeinsam war die Abwendung von der klassizistischen Architektur der Vorkriegszeit unter gleichzeitiger Beibehaltung typischer alpiner Materialien und Elemente unter dem Motto Form follows function. Lois Welzenbacher schrieb 1920 in einem Artikel der Zeitschrift Tyrolean highlands about the architecture of this period:
"As far as we can judge today, it is clear that the 19th century lacked the strength to create its own distinct style. It is the age of stillness... Thus details were reproduced with historical accuracy, mostly without any particular meaning or purpose, and without a harmonious overall picture that would have arisen from factual or artistic necessity."
The best-known and most impressive representative of the so-called Tiroler Moderne was Franz Baumann (1892 - 1974). Unlike Holzmeister or Welzenbacher, he had no academic training. Baumann was born in Innsbruck in 1892, the son of a postal clerk. The theologian, publicist and war propagandist Anton Müllner, alias Bruder Willram became aware of Franz Baumann's talent as a draughtsman and enabled the young man to attend the Staatsgewerbeschule, today's HTL, at the age of 14. It was here that he met his future brother-in-law Theodor Prachensky. Together with Baumann's sister Maria, the two young men went on excursions in the area around Innsbruck to paint pictures of the mountains and nature. During his school years, he gained his first professional experience as a bricklayer at the construction company Huter & Söhne. In 1910 Baumann followed his friend Prachensky to Merano to work for the company Musch & Lun zu arbeiten. Meran war damals Tirols wichtigster Tourismusort mit internationalen Kurgästen. Unter dem Architekten Adalbert Erlebach machte er erste Erfahrungen bei der Planung von Großprojekten wie Hotels und Seilbahnen. Wie den Großteil seiner Generation riss der Erste Weltkrieg auch Baumann aus Berufsleben und Alltag. An der Italienfront erlitt er im Kampfeinsatz einen Bauchschuss, von dem er sich in einem Lazarett in Prag erholte. In dieser ansonsten tatenlosen Zeit malte er Stadtansichten von Bauwerken in und rund um Prag. Diese Bilder, die ihm später bei der Visualisierung seiner Pläne helfen sollten, wurden in seiner einzigen Ausstellung 1919 präsentiert.
Baumann's breakthrough came in the second half of the 1920s. He was able to win the tenders for the remodelling of the Weinhaus Happ in the old town and the Nordkettenbahn railway. In addition to his creativity and ability to think holistically, he was also able to harmonise his architectural approach with the legal situation and the modern requirements of tendering in the 1920s. Construction was a state matter, the Tyrolean Heritage Protection Association together with the district administration, was the final authority responsible for the assessment and authorisation of construction projects. During his time in Merano, Baumann was already involved with the Homeland Security Association came into contact with it. Kunibert Zimmeter had founded this association together with Gotthard Graf Trapp in the final years of the monarchy. In "Our Tyrol. A heritage book" he wrote:
"Let us look at the flattening of our private lives, our amusements, at the centre of which, significantly, is the cinema, at the literary ephemera of our newspaper reading, at the hopeless and costly excesses of fashion in the field of women's clothing, let us take a look at our homes with the miserable factory furniture and all the dreadful products of our so-called gallantry goods industry, Things that thousands of people work to produce, creating worthless bric-a-brac in the process, or let us look at our apartment blocks and villas with their cement façades simulating palaces, countless superfluous towers and gables, our hotels with their pompous façades, what a waste of the people's wealth, what an abundance of tastelessness we must find there."
The economic boom of the late 1920s saw the emergence of a new clientele and clientele that placed new demands on buildings and therefore on the construction industry. In many Tyrolean villages, hotels had replaced churches as the largest building in the townscape. The aristocratic distance from the mountains had given way to a bourgeois enthusiasm for sport. This called for new solutions at new heights. No more grand hotels were built at 1500 m for spa holidays, but a complete infrastructure for skiers in high alpine terrain such as the Nordkette. The Tyrolean Heritage Protection Association ensured that nature and townscape were protected from overly fashionable trends, excessive tourism and ugly industrial buildings. Building projects had to blend harmoniously, attractively and appropriately into the environment. Despite the social and artistic innovations of the time, architects had to keep the typical regional character in mind. This was precisely the strength of Baumann's approach to holistic building in the Tyrolean sense. All technical functions and details, the embedding of the buildings in the landscape, taking into account the topography and sunlight, played a role for him, who was not officially allowed to use the title of architect. He thus followed the "Rules for those who build in the mountains" by the architect Adolf Loos from 1913:
Don't build picturesquely. Leave such effects to the walls, the mountains and the sun. The man who dresses picturesquely is not picturesque, but a buffoon. The farmer does not dress picturesquely. But he is...
Pay attention to the forms in which the farmer builds. For they are ancestral wisdom, congealed substance. But seek out the reason for the mould. If advances in technology have made it possible to improve the mould, then this improvement should always be used. The flail will be replaced by the threshing machine."
Baumann designed even the smallest details, from the exterior lighting to the furniture, and integrated them into his overall concept of the Tiroler Moderne in.
From 1927, Baumann worked independently in his studio in Schöpfstraße in Wilten. He repeatedly came into contact with his brother-in-law and employee of the building authority, Theodor Prachensky. From 1929, the two of them worked together to design the building for the new Hötting secondary school on Fürstenweg. Although boys and girls still had to be planned separately in the traditional way, the building was otherwise completely in keeping with the style of the Neuen Sachlichkeit and the principle Light, air and sun.
In his heyday, he employed 14 people in his office. Thanks to his modern approach, which combined function, aesthetics and economical construction, he survived the economic crisis well. Only the 1000-mark barrier, die Hitler 1934 über Österreich verhängte, um die Republik finanziell in Bredouille zu bringen, brachte sein Architekturbüro wie die gesamte Wirtschaft in Probleme. Nicht nur die Arbeitslosenquote im Tourismus verdreifachte sich innerhalb kürzester Zeit, auch die Baubranche geriet in Schwierigkeiten. 1935 wurde Baumann zum Leiter der Zentralvereinigung für Architekten, nachdem er mit einer Ausnahmegenehmigung ausgestattet diesen Berufstitel endlich tragen durfte. Im gleichen Jahr plante er die Hörtnaglsiedlung in the west of the city.
After the Anschluss in 1938, he quickly joined the NSDAP. On the one hand, like his colleague Lois Welzenbacher, he was probably not averse to the ideas of National Socialism, but on the other he was able to further his career as chairman of the Reich Chamber of Fine Arts in Tyrol. In this position, he courageously opposed the destructive furore with which those in power wanted to change Innsbruck's cityscape, which did not correspond to his idea of urban planning. The mayor of Innsbruck, Egon Denz, wanted to remove the Triumphal Gate and St Anne's Column in order to make more room for traffic in Maria-Theresienstraße. The city centre was still a transit area from the Brenner Pass in the south to reach the main road to the east and west on today's Innrain. At the request of Gauleiter Franz Hofer, a statue of Adolf Hitler was to be erected in place of St Anne's Column. Hofer also wanted to have the church towers of the collegiate church blown up. Baumann's opinion on these plans was negative. When the matter made it to Albert Speer's desk, he agreed with him. From this point onwards, Baumann was no longer awarded any public projects by Gauleiter Hofer.
After being questioned as part of the denazification process, Baumann began working at the city building authority, probably on the recommendation of his brother-in-law Prachensky. Baumann was fully exonerated, among other things by a statement from the Abbot of Wilten, whose church towers he had saved, but his reputation as an architect could no longer be repaired. Moreover, his studio in Schöpfstraße had been destroyed by a bomb in 1944. In his post-war career, he was responsible for the renovation of buildings damaged by the war. Under his leadership, Boznerplatz with the Rudolfsbrunnen fountain was rebuilt as well as Burggraben and the new Stadtsäle (Note: today House of Music).
Franz Baumann died in 1974 and his paintings, sketches and drawings are highly sought-after and highly traded. Anyone who takes a close look at recent major projects such as the city library, the PEMA towers and many of Innsbruck's housing estates will recognise the approaches of the Tiroler Moderne rediscover even today.
Believe, Church and Power
Die Fülle an Kirchen, Kapellen, Kruzifixen und Wandmalereien im öffentlichen Raum wirkt auf viele Besucher Innsbrucks aus anderen Ländern eigenartig. Nicht nur Gotteshäuser, auch viele Privathäuser sind mit Darstellungen der Heiligen Familie oder biblischen Szenen geschmückt. Der christliche Glaube und seine Institutionen waren in ganz Europa über Jahrhunderte alltagsbestimmend. Innsbruck als Residenzstadt der streng katholischen Habsburger und Hauptstadt des selbsternannten Heiligen Landes Tirol wurde bei der Ausstattung mit kirchlichen Bauwerkern besonders beglückt. Allein die Dimension der Kirchen umgelegt auf die Verhältnisse vergangener Zeiten sind gigantisch. Die Stadt mit ihren knapp 5000 Einwohnern besaß im 16. Jahrhundert mehrere Kirchen, die in Pracht und Größe jedes andere Gebäude überstrahlte, auch die Paläste der Aristokratie. Das Kloster Wilten war ein Riesenkomplex inmitten eines kleinen Bauerndorfes, das sich darum gruppierte. Die räumlichen Ausmaße der Gotteshäuser spiegelt die Bedeutung im politischen und sozialen Gefüge wider.
Die Kirche war für viele Innsbrucker nicht nur moralische Instanz, sondern auch weltlicher Grundherr. Der Bischof von Brixen war formal hierarchisch dem Landesfürsten gleichgestellt. Die Bauern arbeiteten auf den Landgütern des Bischofs wie sie auf den Landgütern eines weltlichen Fürsten für diesen arbeiteten. Damit hatte sie die Steuer- und Rechtshoheit über viele Menschen. Die kirchlichen Grundbesitzer galten dabei nicht als weniger streng, sondern sogar als besonders fordernd gegenüber ihren Untertanen. Gleichzeitig war es auch in Innsbruck der Klerus, der sich in großen Teilen um das Sozialwesen, Krankenpflege, Armen- und Waisenversorgung, Speisungen und Bildung sorgte. Der Einfluss der Kirche reichte in die materielle Welt ähnlich wie es heute der Staat mit Finanzamt, Polizei, Schulwesen und Arbeitsamt tut. Was uns heute Demokratie, Parlament und Marktwirtschaft sind, waren den Menschen vergangener Jahrhunderte Bibel und Pfarrer: Eine Realität, die die Ordnung aufrecht hält. Zu glauben, alle Kirchenmänner wären zynische Machtmenschen gewesen, die ihre ungebildeten Untertanen ausnützten, ist nicht richtig. Der Großteil sowohl des Klerus wie auch der Adeligen war fromm und gottergeben, wenn auch auf eine aus heutiger Sicht nur schwer verständliche Art und Weise. Verletzungen der Religion und Sitten wurden in der späten Neuzeit vor weltlichen Gerichten verhandelt und streng geahndet. Die Anklage bei Verfehlungen lautete Häresie, worunter eine Vielzahl an Vergehen zusammengefasst wurde. Sodomie, also jede sexuelle Handlung, die nicht der Fortpflanzung diente, Zauberei, Hexerei, Gotteslästerung – kurz jede Abwendung vom rechten Gottesglauben, konnte mit Verbrennung geahndet werden. Das Verbrennen sollte die Verurteilten gleichzeitig reinigen und sie samt ihrem sündigen Treiben endgültig vernichten, um das Böse aus der Gemeinschaft zu tilgen. Bis in die Angelegenheiten des täglichen Lebens regelte die Kirche lange Zeit das alltägliche Sozialgefüge der Menschen. Kirchenglocken bestimmten den Zeitplan der Menschen. Ihr Klang rief zur Arbeit, zum Gottesdienst oder informierte als Totengeläut über das Dahinscheiden eines Mitglieds der Gemeinde. Menschen konnten einzelne Glockenklänge und ihre Bedeutung voneinander unterscheiden. Sonn- und Feiertage strukturierten die Zeit. Fastentage regelten den Speiseplan. Familienleben, Sexualität und individuelles Verhalten hatten sich an den von der Kirche vorgegebenen Moral zu orientieren. Das Seelenheil im nächsten Leben war für viele Menschen wichtiger als das Lebensglück auf Erden, war dies doch ohnehin vom determinierten Zeitgeschehen und göttlichen Willen vorherbestimmt. Fegefeuer, letztes Gericht und Höllenqualen waren Realität und verschreckten und disziplinierten auch Erwachsene.
Während das Innsbrucker Bürgertum von den Ideen der Aufklärung nach den Napoleonischen Kriegen zumindest sanft wachgeküsst wurde, blieb der Großteil der Menschen weiterhin der Mischung aus konservativem Katholizismus und abergläubischer Volksfrömmigkeit verbunden. Religiosität war nicht unbedingt eine Frage von Herkunft und Stand, wie die gesellschaftlichen, medialen und politischen Auseinandersetzungen entlang der Bruchlinie zwischen Liberalen und Konservativ immer wieder aufzeigten. Seit der Dezemberverfassung von 1867 war die freie Religionsausübung zwar gesetzlich verankert, Staat und Religion blieben aber eng verknüpft. Die Wahrmund-Affäre, die sich im frühen 20. Jahrhundert ausgehend von der Universität Innsbruck über die gesamte K.u.K. Monarchie ausbreitete, war nur eines von vielen Beispielen für den Einfluss, den die Kirche bis in die 1970er Jahre hin ausübte. Kurz vor dem Ersten Weltkrieg nahm diese politische Krise, die die gesamte Monarchie erfassen sollte in Innsbruck ihren Anfang. Ludwig Wahrmund (1861 – 1932) war Ordinarius für Kirchenrecht an der Juridischen Fakultät der Universität Innsbruck. Wahrmund, vom Tiroler Landeshauptmann eigentlich dafür ausgewählt, um den Katholizismus an der als zu liberal eingestuften Innsbrucker Universität zu stärken, war Anhänger einer aufgeklärten Theologie. Im Gegensatz zu den konservativen Vertretern in Klerus und Politik sahen Reformkatholiken den Papst nur als spirituelles Oberhaupt, nicht aber als weltlich Instanz, an. Studenten sollten nach Wahrmunds Auffassung die Lücke und die Gegensätze zwischen Kirche und moderner Welt verringern, anstatt sie einzuzementieren. Seit 1848 hatten sich die Gräben zwischen liberal-nationalen, sozialistischen, konservativen und reformorientiert-katholischen Interessensgruppen und Parteien vertieft. Eine der heftigsten Bruchlinien verlief durch das Bildungs- und Hochschulwesen entlang der Frage, wie sich das übernatürliche Gebaren und die Ansichten der Kirche, die noch immer maßgeblich die Universitäten besetzten, mit der modernen Wissenschaft vereinbaren ließen. Liberale und katholische Studenten verachteten sich gegenseitig und krachten immer aneinander. Bis 1906 war Wahrmund Teil der Leo-Gesellschaft, die die Förderung der Wissenschaft auf katholischer Basis zum Ziel hatte, bevor er zum Obmann der Innsbrucker Ortsgruppe des Vereins Freie Schule wurde, der für eine komplette Entklerikalisierung des gesamten Bildungswesens eintrat. Vom Reformkatholiken wurde er zu einem Verfechter der kompletten Trennung von Kirche und Staat. Seine Vorlesungen erregten immer wieder die Aufmerksamkeit der Obrigkeit. Angeheizt von den Medien fand der Kulturkampf zwischen liberalen Deutschnationalisten, Konservativen, Christlichsozialen und Sozialdemokraten in der Person Ludwig Wahrmunds eine ideale Projektionsfläche. Was folgte waren Ausschreitungen, Streiks, Schlägereien zwischen Studentenverbindungen verschiedener Couleur und Ausrichtung und gegenseitige Diffamierungen unter Politikern. Die Los-von-Rom Bewegung des Deutschradikalen Georg Ritter von Schönerer (1842 – 1921) krachte auf der Bühne der Universität Innsbruck auf den politischen Katholizismus der Christlichsozialen. Die deutschnationalen Akademiker erhielten Unterstützung von den ebenfalls antiklerikalen Sozialdemokraten sowie von Bürgermeister Greil, auf konservativer Seite sprang die Tiroler Landesregierung ein. Die Wahrmund Affäre schaffte es als Kulturkampfdebatte bis in den Reichsrat. Für Christlichsoziale war es ein „Kampf des freissinnigen Judentums gegen das Christentum“ in dem sich „Zionisten, deutsche Kulturkämpfer, tschechische und ruthenische Radikale“ in einer „internationalen Koalition“ als „freisinniger Ring des jüdischen Radikalismus und des radikalen Slawentums“ präsentierten. Wahrmund hingegen bezeichnete in der allgemein aufgeheizten Stimmung katholische Studenten als „Verräter und Parasiten“. Als Wahrmund 1908 eine seiner Reden, in der er Gott, die christliche Moral und die katholische Heiligenverehrung anzweifelte, in Druck bringen ließ, erhielt er eine Anzeige wegen Gotteslästerung. Nach weiteren teils gewalttätigen Versammlungen sowohl auf konservativer und antiklerikaler Seite, studentischen Ausschreitungen und Streiks musste kurzzeitig sogar der Unibetrieb eingestellt werden. Wahrmund wurde zuerst beurlaubt, später an die deutsche Universität Prag versetzt.
Auch in der Ersten Republik war die Verbindung zwischen Kirche und Staat stark. Der christlichsoziale, als Eiserner Prälat in die Geschichte eingegangen Ignaz Seipel schaffte es in den 1920er Jahren bis ins höchste Amt des Staates. Bundeskanzler Engelbert Dollfuß sah seinen Ständestaat als Konstrukt auf katholischer Basis als Bollwerk gegen den Sozialismus. Auch nach dem Zweiten Weltkrieg waren Kirche und Politik in Person von Bischof Rusch und Kanzler Wallnöfer ein Gespann. Erst dann begann eine ernsthafte Trennung. Glaube und Kirche haben noch immer ihren fixen Platz im Alltag der Innsbrucker, wenn auch oft unbemerkt. Die Kirchenaustritte der letzten Jahrzehnte haben der offiziellen Mitgliederzahl zwar eine Delle versetzt und Freizeitevents werden besser besucht als Sonntagsmessen. Die römisch-katholische Kirche besitzt aber noch immer viel Grund in und rund um Innsbruck, auch außerhalb der Mauern der jeweiligen Klöster und Ausbildungsstätten. Etliche Schulen in und rund um Innsbruck stehen ebenfalls unter dem Einfluss konservativer Kräfte und der Kirche. Und wer immer einen freien Feiertag genießt, ein Osterei ans andere peckt oder eine Kerze am Christbaum anzündet, muss nicht Christ sein, um als Tradition getarnt im Namen Jesu zu handeln.
A republic is born
Few eras are more difficult to grasp than the interwar period. The Roaring TwentiesJazz and automobiles come to mind, as do inflation and the economic crisis. In big cities like Berlin, young ladies behaved as Flappers mit Bubikopf, Zigarette und kurzen Röcken zu den neuen Klängen lasziv, Innsbrucks Bevölkerung gehörte als Teil der jungen Republik Österreich zum größten Teil zur Fraktion Armut, Wirtschaftskrise und politischer Polarisierung. Schon die Ausrufung der Republik am Parlament in Wien vor über 100.000 mehr oder minder begeisterten, vor allem aber verunsicherten Menschen verlief mit Tumulten, Schießereien, zwei Toten und 40 Verletzten alles andere als reibungsfrei. Wie es nach dem Ende der Monarchie und dem Wegfall eines großen Teils des Staatsterritoriums weitergehen sollte, wusste niemand. Das neue Österreich erschien zu klein und nicht lebensfähig. Der Beamtenstaat des k.u.k. Reiches setzte sich nahtlos unter neuer Fahne und Namen durch. Die Bundesländer als Nachfolger der alten Kronländer erhielten in der Verfassung im Rahmen des Föderalismus viel Spielraum in Gesetzgebung und Verwaltung. Die Begeisterung für den neuen Staat hielt sich aber in der Bevölkerung in Grenzen. Nicht nur, dass die Versorgungslage nach dem Wegfall des allergrößten Teils des ehemaligen Riesenreiches der Habsburger miserabel war, die Menschen misstrauten dem Grundgedanken der Republik. Die Monarchie war nicht perfekt gewesen, mit dem Gedanken von Demokratie konnten aber nur die allerwenigsten etwas anfangen. Anstatt Untertan des Kaisers war man nun zwar Bürger, allerdings nur Bürger eines Zwergstaates mit überdimensionierter und in den Bundesländern wenig geliebter Hauptstadt anstatt eines großen Reiches. In den ehemaligen Kronländern, die zum großen Teil christlich-sozial regiert wurden, sprach man gerne vom Viennese water headwho was fed by the yields of the industrious rural population.
Other federal states also toyed with the idea of seceding from the Republic after the plan to join Germany, which was supported by all parties, was prohibited by the victorious powers of the First World War. The Tyrolean plans, however, were particularly spectacular. From a neutral Alpine state with other federal states, a free state consisting of Tyrol and Bavaria or from Kufstein to Salurn, an annexation to Switzerland and even a Catholic church state under papal leadership, there were many ideas. The most obvious solution was particularly popular. In Tyrol, feeling German was nothing new. So why not align oneself politically with the big brother in the north? This desire was particularly pronounced among urban elites and students. The annexation to Germany was approved by 98% in a vote in Tyrol, but never materialised.
Instead of becoming part of Germany, they were subject to the unloved Wallschen. Italian troops occupied Innsbruck for almost two years after the end of the war. At the peace negotiations in Paris, the Brenner Pass was declared the new border. The historic Tyrol was divided in two. The military was stationed at the Brenner Pass to secure a border that had never existed before and was perceived as unnatural and unjust. In 1924, the Innsbruck municipal council decided to name squares and streets around the main railway station after South Tyrolean towns. Bozner Platz, Brixnerstrasse and Salurnerstrasse still bear their names today. Many people on both sides of the Brenner felt betrayed. Although the war was far from won, they did not see themselves as losers to Italy. Hatred of Italians reached its peak in the interwar period, even if the occupying troops were emphatically lenient. A passage from the short story collection "The front above the peaks" by the National Socialist author Karl Springenschmid from the 1930s reflects the general mood:
"The young girl says, 'Becoming Italian would be the worst thing.
Old Tappeiner just nods and grumbles: "I know it myself and we all know it: becoming a whale would be the worst thing."
Trouble also loomed in domestic politics. The revolution in Russia and the ensuing civil war with millions of deaths, expropriation and a complete reversal of the system cast its long shadow all the way to Austria. The prospect of Soviet conditions machte den Menschen Angst. Österreich war tief gespalten. Hauptstadt und Bundesländer, Stadt und Land, Bürger, Arbeiter und Bauern – im Vakuum der ersten Nachkriegsjahre wollte jede Gruppe die Zukunft nach ihren Vorstellungen gestalten. Die Kulturkämpfe der späten Monarchie zwischen Konservativen, Liberalen und Sozialisten setzte sich nahtlos fort. Die Kluft bestand nicht nur auf politischer Ebene. Moral, Familie, Freizeitgestaltung, Erziehung, Glaube, Rechtsverständnis – jeder Lebensbereich war betroffen. Wer sollte regieren? Wie sollten Vermögen, Rechte und Pflichten verteilt werden. Ein kommunistischer Umsturz war besonders in Tirol keine reale Gefahr, ließ sich aber medial gut als Bedrohung instrumentalisieren, um die Sozialdemokratie in Verruf zu bringen. 1919 hatte sich in Innsbruck zwar ein Workers', farmers' and soldiers' council nach sowjetischem Vorbild ausgerufen, sein Einfluss blieb aber gering und wurde von keiner Partei unterstützt. Ab 1920 bildeten sich offiziell sogenannten Soldatenräte, die aber christlich-sozial dominiert waren. Das bäuerliche und bürgerliche Lager rechts der Mitte militarisierte sich mit der Tiroler Heimatwehr professioneller und konnte sich über stärkeren Zulauf freuen als linke Gruppen, auch dank kirchlicher Unterstützung. Die Sozialdemokratie wurde von den Kirchkanzeln herab und in konservativen Medien als Jewish Party and homeless traitors to their country. They were all too readily blamed for the lost war and its consequences. The Tiroler Anzeiger summarised the people's fears in a nutshell: "Woe to the Christian people if the Jews=Socialists win the elections!".
With the new municipal council regulations of 1919, which provided for universal suffrage for all adults, the Innsbruck municipal council comprised 40 members. Of the 24,644 citizens called to the ballot box, an incredible 24,060 exercised their right to vote. Three women were already represented in the first municipal council with free elections. While in the rural districts the Tyrolean People's Party as a merger of Farmers' Union, People's Association und Catholic Labour Despite the strong headwinds in Innsbruck, the Social Democrats under the leadership of Martin Rapoldi were always able to win between 30 and 50% of the vote in the first elections in 1919. The fact that the Social Democrats did not succeed in winning the mayor's seat was due to the majorities in the municipal council formed by alliances with other parties. Liberals and Tyrolean People's Party was at least as hostile to social democracy as he was to the federal capital Vienna and the Italian occupiers.
But high politics was only the framework of the actual misery. The as Spanish flu This epidemic, which has gone down in history, also took its toll in Innsbruck in the years following the war. Exact figures were not recorded, but the number of deaths worldwide is estimated at 27 - 50 million. In Innsbruck, at the height of the Spanish flu epidemic, it is estimated that around 100 people fell victim to the disease every day. Many Innsbruck residents had not returned home from the battlefields and were missing as fathers, husbands and labourers. Many of those who had made it back were wounded and scarred by the horrors of war. As late as February 1920, the „Tyrolean Committee of the Siberians" im Gasthof Breinößl "...in favour of the fund for the repatriation of our prisoners of war..." organised a charity evening. Long after the war, the province of Tyrol still needed help from abroad to feed the population. Under the heading "Significant expansion of the American children's aid programme in Tyrol" was published on 9 April 1921 in the Innsbrucker Nachrichten to read: "Taking into account the needs of the province of Tyrol, the American representatives for Austria have most generously increased the daily number of meals to 18,000 portions.“
Then there was unemployment. Civil servants and public sector employees in particular lost their jobs after the League of Nations linked its loan to severe austerity measures. Salaries in the public sector were cut. There were repeated strikes. Tourism as an economic factor was non-existent due to the problems in the neighbouring countries, which were also shaken by the war. The construction industry, which had been booming before the war, collapsed completely. Innsbruck's largest company Huter & Söhne hatte 1913 über 700 Mitarbeiter, am Höhepunkt der Wirtschaftskrise 1933 waren es nur noch 18. Der Mittelstand brach zu einem guten Teil zusammen. Der durchschnittliche Innsbrucker war mittellos und mangelernährt. Oft konnten nicht mehr als 800 Kalorien pro Tag zusammengekratzt werden. Die Kriminalitätsrate war in diesem Klima der Armut höher als je zuvor. Viele Menschen verloren ihre Bleibe. 1922 waren in Innsbruck 3000 Familien auf Wohnungssuche trotz eines städtischen Notwohnungsprogrammes, das bereits mehrere Jahre in Kraft war. In alle verfügbaren Objekte wurden Wohnungen gebaut. Am 11. Februar 1921 fand sich in einer langen Liste in den Innsbrucker Nachrichten on the individual projects that were run, including this item:
„The municipal hospital abandoned the epidemic barracks in Pradl and made them available to the municipality for the construction of emergency flats. The necessary loan of 295 K (note: crowns) was approved for the construction of 7 emergency flats.“
Very little happened in the first few years. Then politics awoke from its lethargy. The crown, a relic from the monarchy, was replaced by the schilling as Austria's official currency on 1 January 1925. The old currency had lost more than 95% of its value against the dollar between 1918 and 1922, or the pre-war exchange rate. Innsbruck, like many other Austrian municipalities, began to print its own money. The amount of money in circulation rose from 12 billion crowns to over 3 trillion crowns between 1920 and 1922. The result was an epochal inflation.
With the currency reorganisation following the League of Nations loan under Chancellor Ignaz Seipel, not only banks and citizens picked themselves up, but public building contracts also increased again. Innsbruck modernised itself. There was what economists call a false boom. This short-lived economic recovery was a Bubble, However, the city of Innsbruck was awarded major projects such as the Tivoli, the municipal indoor swimming pool, the high road to the Hungerburg, the mountain railways to the Isel and the Nordkette, new schools and apartment blocks. The town bought Lake Achensee and, as the main shareholder of TIWAG, built the power station in Jenbach. The first airport was built in Reichenau in 1925, which also involved Innsbruck in air traffic 65 years after the opening of the railway line. In 1930, the university bridge connected the hospital in Wilten and the Höttinger Au. The Pembaur Bridge and the Prince Eugene Bridge were built on the River Sill. The signature of the new, large mass parties in the design of these projects cannot be overlooked.
The first republic was a difficult birth from the remnants of the former monarchy and it was not to last long. Despite the post-war problems, however, a lot of positive things also happened in the First Republic. Subjects became citizens. What began in the time of Maria Theresa was now continued under new auspices. The change from subject to citizen was characterised not only by a new right to vote, but above all by the increased care of the state. State regulations, schools, kindergartens, labour offices, hospitals and municipal housing estates replaced the benevolence of the landlord, sovereigns, wealthy citizens, the monarchy and the church.
To this day, much of the Austrian state and Innsbruck's cityscape and infrastructure are based on what emerged after the collapse of the monarchy. In Innsbruck, there are no conscious memorials to the emergence of the First Republic in Austria. The listed residential complexes such as the Slaughterhouse blockthe Pembaurblock or the Mandelsbergerblock oder die Pembaur School are contemporary witnesses turned to stone. Every year since 1925, World Savings Day has commemorated the introduction of the schilling. Children and adults should be educated to handle money responsibly.